Machining
The processes of machining are based on cutting a work-piece in order to change its shape while removing the excess material. The main and most common machining processes are turning, drilling and milling. Other processes are called miscellaneous operations, which consist of shaping, boring, sawing, planing, and broaching.
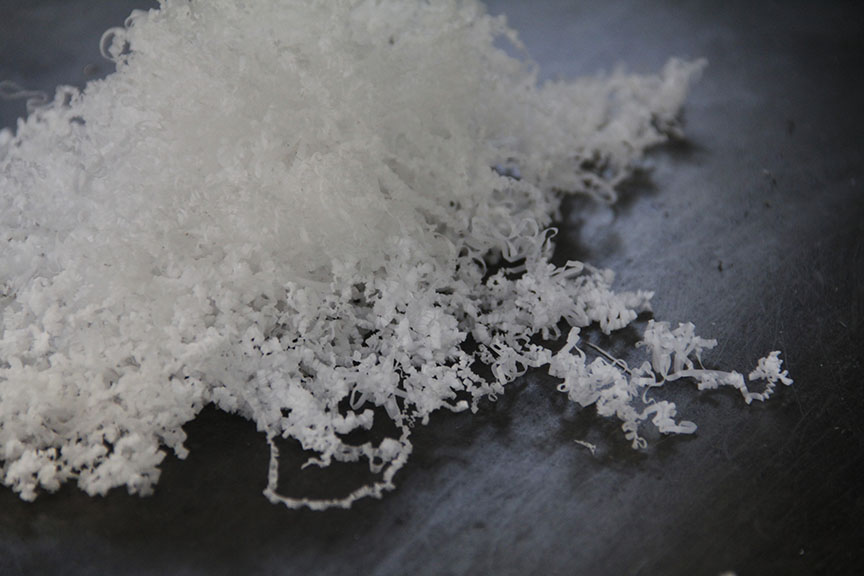
All machining processes (except some miscellaneous operations) produce swarf (also called chips) which consists of small pieces of the machined material which were removed during the process while the cutting tool was applying stress on the material. It is the residue of the original work-piece. Its shape differs according to the used process and tools.

Cutting and Cutting Tools
Each machining process uses a specialized cutting tool. There are two basic types of these tools. The first ones are simple point tools which are used for turning, planing and boring processes, and the second ones are multi-point tools which are used for milling and drilling. Cutting tools are usually made from carbide and high-speed steel. Upkeep of cutting tools can be very expensive, but it is important for the tools to stay in good condition, so the work-piece is cut correctly.
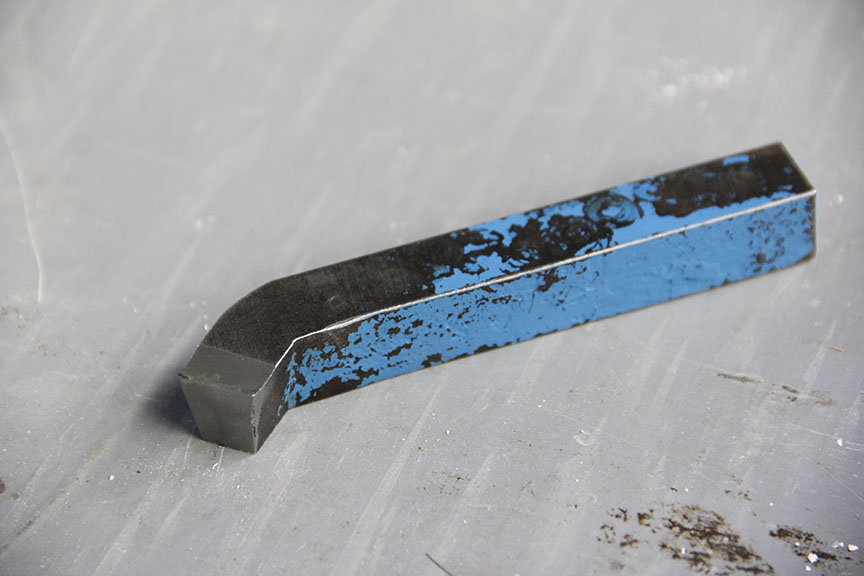

To finish the work-piece, we usually perform multiple cuts. The whole process can be divided into two sections: the roughing phase and the finishing phase. Roughing cuts are used to change the form of the material according to the desired shape of the final product. The last cut is called the finishing cut which is used to finish the surface of the work-piece while it gains the exact desired dimensions. Sometimes it might be necessary to use cutting fluid which lubricates and cools the cutting tool.
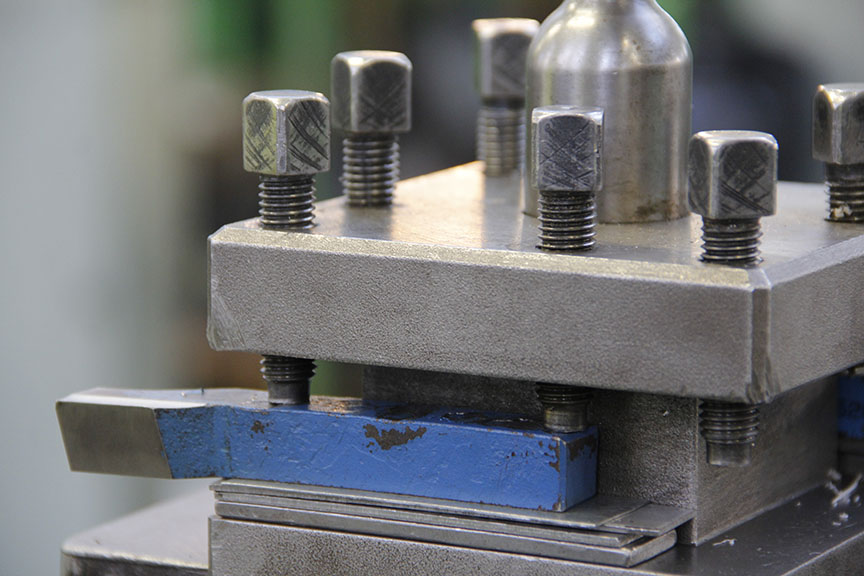
Turning
Turning is exclusively used for work-pieces having circular cross-section. It employs the cutting tool moving towards a rotating work-piece fixed in a machine called lathe. The tool may have a different shape and angle of the blade according to the specific operation. The process is done manually, but it can be automated with the use of Computer Numerical Control (CNC), where all the movements are done by a computer using instructions which were made by us in advance.

If we use turning on the internal surfaces of the work-piece, we do not call this process turning anymore. Internal turning is usually referred to as boring. Boring is commonly used to create work-pieces with a tubular shape.
If the cutting tool cuts the end of the used material, we usually call it facing instead. This generally occurs at the beginning and the end of the turning process.
Drilling
Drilling employs a tool called a drill bit and is conducted on a drilling machine. The bit rotates in order to drill through the used work-piece. The drill has a shape which helps eliminate swarf. If we widen an already made hole, the process is called boring (similarly to internal turning). We can use a tool called holesaw if the hole has a large diameter. Holesaw has a cylindrical shape with teeth. We are able to drill into concrete with the use of holesaws whose edges are made of industrial diamond. This process is called core drilling or diamond drilling. Drilling can be automated by CNC.
There are various drill bits which can be used if needed, such as peck drills, spotting drills or chucking reamers. Peck drill bits are used when we frequently retract the bit back in order to lower drifting of the drilling. Spotting drill bits are used to drill shallow holes. Chucking reamers are used for boring with exceptional precision and accuracy.
Milling
Milling employs rotating multi-point cutters which are typically stationary. The cutters are toothed disc-like tools. The used work-piece is fixed onto a table which is part of a milling machine. The table of the milling machine is then moved against the rotation of the cutters, so the material is cut by them. For CNC milling is typical to move the material in the direction of the cutter rotation.
Milling can be divided into two categories. The first one is face milling which we use to cut flat surfaces or cavities with flat bottom into the material. The second one is peripheral milling which is used when gear teeth, deep slots or threads are required to be made.
The milling machine is able to perform various other processes such as planing, routing, die-sinking, etc. Most milling machines have either vertically or horizontally mounted cutters with the exception of universal milling machines which can have both.
Sawing
Sawing employs a thin toothed blade which cuts the material while reducing its thickness. The slit left on the work-piece after cutting is called a kerf. Other sawing tools include circular saws, band saws, and power hacksaws. Compared to the other tools, the hacksaws have much smaller teeth.
Computer Numerical Control
CNC is computer software used to automate machining processes. With its use, it is very easy manufacture complex work-pieces with very good precision.
CNC programmers who operate the program can choose where to cut on the virtual representation of the work-piece. They have to choose which tools to use on every selected cut. After this, the automated machining processes are ready to be started.